Calcitriol is the active form of Vitamin D. It is also known as 1,25(OH)2D. Calcitriol has long been known for its important role in regulating body levels of calcium and phosphorus, and in mineralization of bone.
Functions of Calcitriol:
- Involved in the intestinal absorption of calcium and the regulation of calcium homeostasis, bone differentiation and immune response.
- Increase renal tubular reabsorption of calcium and hence reducing the loss of calcium in the urine.
- Stimulating release of calcium from bone.
Understanding Vitamin D Metabolism & Function:
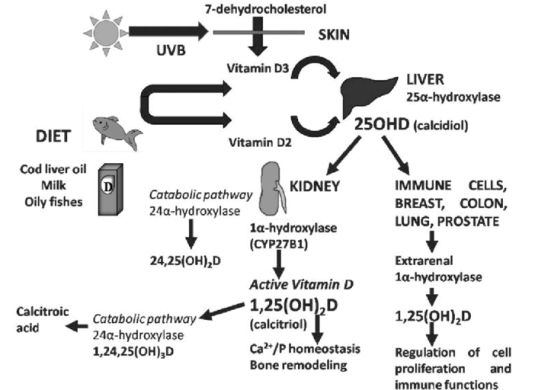
The entry of vitamin D into the body is through the production of vitamin D in the skin upon exposure to sunlight (UVB) and through ingestion of either foods containing cholecalciferol (vitamin D3,) or ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) or dietary supplements of these substances.
The storage type of vitamin D, namely 25- hydroxy vitamin D (Calcidiol), is formed in the liver. This is the major circulating form of vitamin D, and the form that is currently used as a measure of one’s vitamin D status.
The hormone 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D (Calcitriol) is formed in a second step in the kidney. The responsible enzyme, the kidney 1 α-hydroxylase, is subjected to a rigid control through hormones [especially PTH (parathyroid hormone)] and its activity is influenced by the serum concentrations of calcium and phosphate.
Importance of testing for Calcitriol levels:
- Calcitriol assessment may be beneficial in patients with chronic kidney failure. Diminished levels of calcitriol can be seen in patients with kidney failure.
- Calcitriol may also be helpful in the diagnosis of parathyroid function disorders.
References:
- Holick MF. Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J Med. 2007 Jul 19; 357(3):266-281. PubMed 17634462
- Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrare HA, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Jul; 96(7):1911-1930. PubMed 21646368
- Norman AW. From vitamin D to hormone D: Fundamentals of the vitamin D endocrine system essential for good health. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008 Aug; 88(2):491S-499S. PubMed 18689389
- Llach F, Velasquez Forero F. Secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic renal failure: Pathogenic and clinical aspects. Am J Kidney Dis 2001 Nov; 38(5 Suppl 5): S20–S33. PubMed 11689384
- Malloy PJ, Feldman D. Genetic disorders and defects in vitamin D action. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.2010 Jun; 39(2):333-346. PubMed 20511055
- Bikle DD. Vitamin D metabolism, mechanism of action, and clinical applications. Chem Biol. 2014 Mar 20; 21(3):319-329. PubMed 24529992
Disclaimer:
The information on healthmatters.io is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.

