- RDW stands for “Red Cell Distribution Width“.
- RDW is usually part of a complete blood count test.
The RDW value tells you whether enough of your red blood cells are of normal size and shape.

Why is this important?
The red blood cells are usually flat and lenticular (disc-shaped) with a diameter of around 7.5 µm (micrometer).

What’s the function of red blood cells?
The sole function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen to different parts of the body.
Let’s describe a few terms first:
Blood Vessels:
Blood vessels are anything that carries blood. There are three major types of blood vessels:
- Arteries,
- veins, and
- capillaries.

Let’s take a closer look at arteries and veins:
Arteries are blood vessels responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the body. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood low in oxygen from the body back to the heart for re-oxygenation.
Arteries are usually indicated in red and veins in blue.

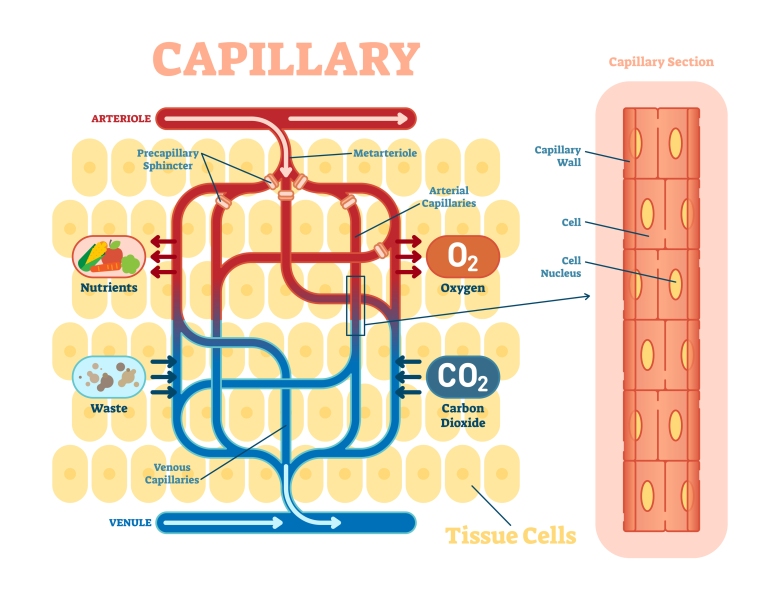
Capillaries:
Capillaries are tiny blood vessels connecting arteries to veins. These blood vessels carry oxygen and nutrients to individual cells throughout the body.
 OK, back to the red blood cells and their distribution width:
OK, back to the red blood cells and their distribution width:
Blood cells must squeeze through the body’s smallest blood vessels, the above described capillaries, to do their job, but capillaries often become narrower than the cells in their normal disc shape. Capillaries can be as small as 4 µm in diameter. So the cells must deform and “curl up” to fit through those capillaries. Remember a normal red blood cell is around 7.5 µm in diameter.
Only when this process of “squeezing” through capillaries can happen, the supply of oxygen is guaranteed throughout the whole body.
Some red blood cells are however not optimally formed. To a certain extent this is normal as there are 2 million red blood cells formed per second. Usually there are around 85% to 89% of red blood cells developed properly.
By looking at the red cell distribution width value one can see how many red blood cells have a deviating form factor. If 85% to 89% are usually normally developed the RDW value then should range between 11% and 15%.
What are RDW-SD and RDW-CV markers?
RDW-SD and RDW-CV are parameters that are analyzed as part of the red blood cell blood analysis:
One important factor to mention now is that when we are looking at the red cell distribution width, we are not looking at the actual width (or diameter) of the individual red blood cells. We are looking at the width of the curve that the blood analyzing machine spits out.
So a higher or lower RDW-CV value would not indicate how much bigger or smaller the actual red blood cells are (=diameter), but rather how big the variation in cell size and volume is.
Here is how a sample volume curve would look like:

Mathematically, the RDW-CV is calculated with the following formula:
Let’s look at this formula a little closer:
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV), also called mean cell volume, is a measure of the average volume of a red blood cell. The normal range of a MCV value ranges between 80 to 96 fl (=femtoliter). This means that on average a red blood cell volume is, let’s say, 90 fl. If now the standard deviation from this curve is, let’s say, 10 fl then the RDW-CV value would be 11.1% and therefore in the normal range.
The RDW-SD is an actual measurement of the width of the red cell distribution curve in femtoliters (fL) and not percent. The width of the distribution curve is measured at the point that is 20% above the baseline (aka frequency level). Since the RDW-SD is an actual measurement, it is not influenced by the MCV and more accurately reflects the red cell size variance. The RDW-SD normal value, which is the width of the volume curve, is between 39 and 46 fL.
What if my RDW results are normal?
A person with a normal result may still have an underlying condition. Doctors often compare RDW results with those of a mean cell volume (MCV) test.
Results may show:
- Normal RDW and normal MCV
- People with normal results may still have anemia caused by a chronic medical condition or blood loss.
- Normal RDW and low MCV
- This combination may indicate anemia caused by a chronic condition or thalassemia (a blood disorder in which the body makes an abnormal form of hemoglobin).
- Normal RDW and high MCV
- This can indicate a liver condition or alcohol abuse. Or, a person may have this result because they are on antiviral drugs or chemotherapy. If other blood characteristics are also affected, this can suggest aplastic anemia, a rare disorder caused by inadequate blood cell production.
What if my RDW count is high?
If your red blood cells are unequal in size this is called anisocytosis. “Aniso” means unequal, and “cytosis” refers the characteristics, features and the number of cells.
Anisocytosis itself is a nonspecific term, as there are several different ways in which cells can be unequal.
The condition is prominent in cases of iron deficiency anemia. Iron is mostly stored in red blood cells, which help carry and store oxygen in the blood. A lack of iron in the blood leads to a reduction of red blood cells.
Symptoms of anisocytosis:
When the shape and size of red blood cells are not correct, then oxygen is not being transported around the body as efficiently as it should be.
This can lead to:
- tiredness
- shortness of breath
- dizziness
- headache
- cold hands and feet
- pale skin
- chest pain
A person may have:
- High RDW and normal MCV
- This suggests a deficiency of iron, B-12, or folate. It may also indicate chronic liver disease.
- High RDW and low MCV
- This suggests iron deficiency or microcytic anemia.
- High RDW and high MCV.
- This indicates a lack of B-12 or folate. It can also suggest macrocytic anemia or chronic liver disease.
To confirm a diagnosis, a doctor will compare the results of the RDW test with those of the MCV measurement.
What if my RDW count is low?
A low RDW means that the red blood cells vary little in size. This could be due to the following:
- Macrocytic anemia
- A blood disorder in which not enough RBCs are produced, but the ones that are present are large.
- Microcytic anemia
- A condition in which lots of small red blood cells are present.
In these two disorders the red blood cells do not vary much in size because they are either all small or all large.
References:
- BAIN, B. J. Diagnosis from the blood smear. N Engl J Med, v. 353, n. 5, p. 498-507, 2005.
- BARNES, P. W. et al. The international consensus group for hematology review: suggested criteria for action following automated CBC and WBC differential analysis. Lab Hematol, v. 11, n. 2, p. 83-90, 2005.
- BESSMAN, J. A. Red cells. In: BESSMAN, J. A. (Ed.). Automated blood counts and differentials: a practical guide. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1986. p. 5-56.
- BUTTARELLO, M.; PLEBANI, M. Automated blood cell counts: state of the art. Am J Clin Pathol, v. 130, n. 1, p. 104-16, 2008.
- CAPORAL, F. A.; COMAR, S. R. Evaluation of RDW-CV, RDW-SD, and MATH-1SD for the detection of erythrocyte size heterogeneity observed by optical microscopy. Int J Lab Hematol, v. 35, suppl. 1, p. 44, 2013.
Disclaimer:
The information on healthmatters.io is NOT intended to replace a one-on-one relationship with a qualified health care professional and is not intended as medical advice.

So if someone with a low mcv has an RDW-CV that’s high and their RDW-SD is low, is the RDW-CV falsely increased then?